MIL-STD-810G
PERFECTRON’s Stack Rack series rugged computers – SR100, SR200, and SR700 are designed to meet the strict standards of MIL-STD 810G. When it comes to true ruggedness, MIL-STD-810G standard is considered the upmost principle. Originally established by the US government to simulate how materials would hold up to harsh environments, It provides a series of testing procedures for resistance to shock, vibration, dust, humidity, and extreme temperatures.
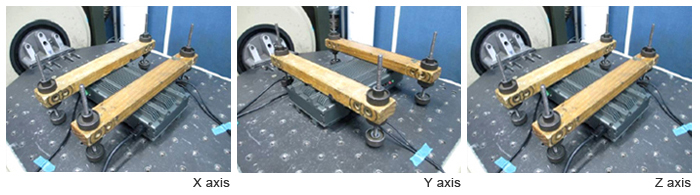
- 1. Vibration
-
MIL-STD-810G Test Method 514.6 Vibration Procedure IV Non-Operating
MIL-STD-810G Test Method 514.6 Vibration Procedure III Operating
Vibration test is conducted to create an environment, in which long-term and high level vibration is simulated. The test is performed with both the system operating/non. Various levels and duration of vibration is simulated in three axis (X, Y, and Z), with up to 7g transitions.
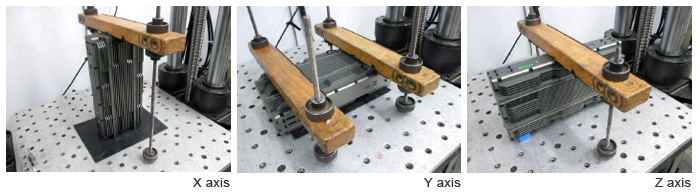
- 2. Mechanical Shock
-
MIL-STD-810G Test Method 516.6 Shock-Procedure IV Non-Operating
MIL-STD-810G Test Method 516.6 Shock-Procedure III Operating
Mechanical Shock test is conducted to ensure that equipment can withstand drops encountered during handling, transportation, and normal use. The test is performed with both the system operating/non. We expose the system to 3 pulses/direction of sawtooth shock at 100g 11ms. 6 directions for a total of 18 pulses.
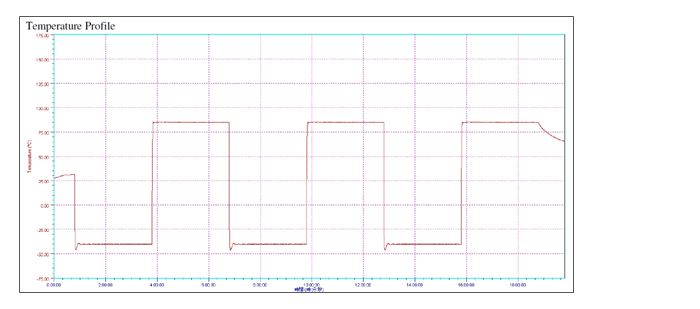
- 3. Temperature Shock
-
MIL-STD-810G Test Method 503.5 Temperature Shock Procedure I-C / Storage (Multi-cycle shocks from constant extreme temperature, From 85℃ to -40℃, Three cycles)
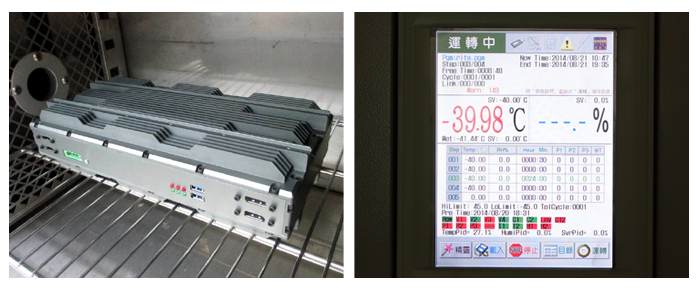
Temperature Shock test, also named Thermal Shock test, is to ensure that systems can thrive even in extreme temperature range. We place the system at ambient temperature into chamber at -40℃ and stabilize it, then transfer in less than 1 minute to chamber at +85℃ and stabilize. Return the system to ambient temperature and perform operational check.

- 4. High Temperature
-
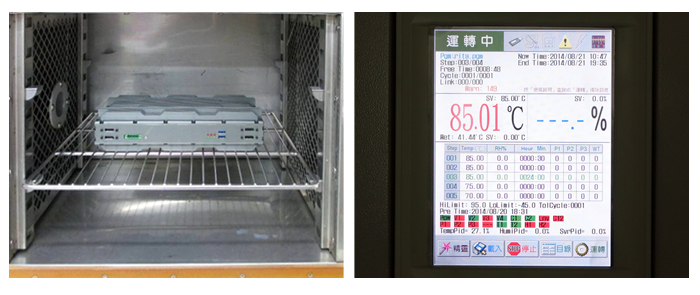
MIL-STD-810G Test Method 501.5 high Temp ( 96 hours @75℃ non-operating + 72 hours @ 75℃ operating )
This testing method is broken down into two procedures.
Procedure I (storage) exposes the system to high temperatures while it is turned off, and its purpose is to test the durability of the materials that make up the system. The chamber temperature is 75℃ and the test duration is 96 hours.
Procedure II (operation) is to test how the device puts up with heat while having it turned on and used.
The chamber temperatures used in an operational cyclical test is 75℃, and the test duration is 72 hours. The temperature needs to cycle from one end to the other a minimum of three times while testing that the device functions at every point in the test.
-
5. Low Temperature
-
IL-STD-810G Test Method 502.5 Low Temp ( 96 hours @ -40℃ non-operating +72 hours @ -40℃ operating )
There are two parts in this test to determine whether the system can persevere in extremely cold environment.
Procedure I (storage) exposes the system to low temperatures while it is turned off, and its purpose is to test the durability of the materials that make up the system. The chamber temperature is -40℃ and the test duration is 96 hours.
Procedure II (operation) testing involves slowly cooling the device to the low temperature and leaving it at that temperature for at least two hours, checking to see that it is still functioning during that time. The chamber temperature is -40℃ and the test duration is 72 hours.